Photodynamic therapy in periodontology
The health of our oral cavity is directly linked to the overall health of our body, as untreated teeth often become a dangerous source of chronic infection. This infection can not only spread to nearby areas but also harm internal organs. Therefore, it is crucial to take care of your teeth and gums, not just for aesthetic reasons.
To address gum diseases and periodontal issues, which refer to the tissues surrounding the teeth and securing their position, a periodontist can help. If you are experiencing any unpleasant symptoms, make an appointment for a free consultation. In the meantime, let’s talk more about periodontology.
What is Periodontology?
Periodontology is a field in modern dentistry aimed at treating the gums and the surrounding tissues of the tooth. Periodontal services have become highly sought after due to the fact that neglected gum diseases are often the cause of tooth loss. For example, many people do not take gum bleeding seriously, which is the first indicator that professional treatment is needed. It is important not to delay, as healthy teeth may be lost in the process.
The primary goal of periodontal diagnostics and treatment is to restore and maintain the health of the gums and the bone tissue surrounding the teeth. To prevent gum disease, it is important to: maintain daily oral hygiene, undergo professional cleaning every six months, and seek treatment if you experience increased tooth sensitivity, enamel discoloration, gum recession, excessive tooth exposure, inflammation of the gums, or if the gums do not fit tightly to the tooth.
Causes of Periodontal Diseases
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Improper diet – lack of certain vitamins and minerals in the diet can trigger inflammatory processes in the periodontium.
- Improper oral hygiene – insufficient care for teeth can lead to the rapid growth of bacteria in the mouth, while improper brushing can cause mechanical damage to tissues.
- Decreased immunity – stress, chronic fatigue can reduce immunity, fostering the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Improper bite and jaw anomalies – these complicate oral hygiene procedures.
- Presence of tartar and plaque – sources of infection that lead to chronic gum inflammation.
- Substandard dental prosthetics – low-quality or improperly installed prosthetics can injure periodontal tissues, leading to chronic inflammation.
This pathology is also more common in older patients, as it is related to degenerative processes in periodontal tissues.
Gum Diseases and Their Symptoms
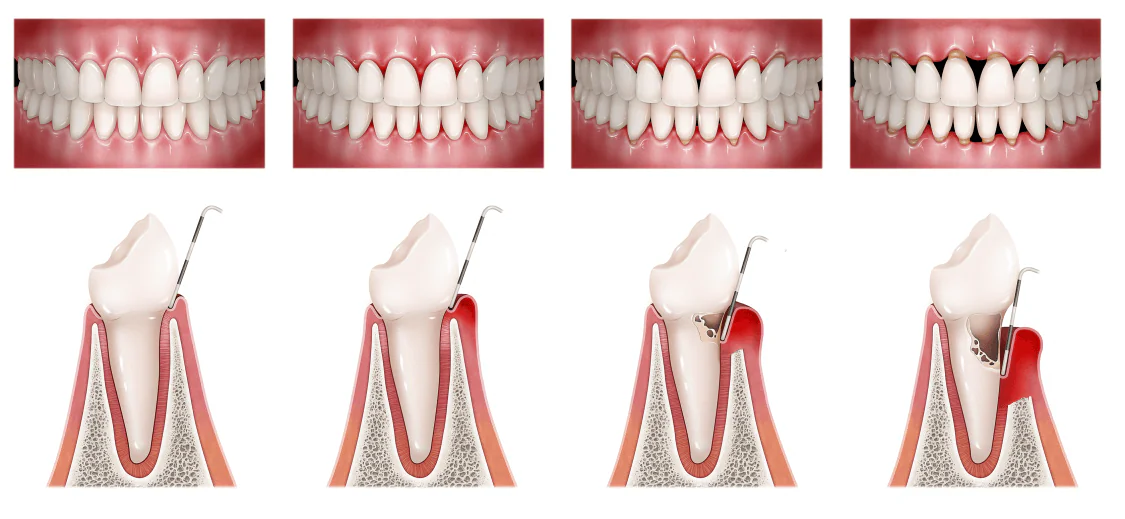
Gum diseases are caused by bacterial infections, which affect the surfaces of teeth and result in plaque buildup. If untreated, inflammation can lead to irreversible destructive changes, such as gum recession. Bacteria multiply and release toxins that damage the tissues surrounding the tooth. As a result, an infected periodontal pocket forms, and periodontitis begins.
The most common periodontal diseases include:
- Gingivitis: Inflammation of the tissues in contact with the tooth. The most common issue, often due to poor oral care. If left untreated, it can quickly progress to periodontitis.
- Periodontitis: Acute gum inflammation. If untreated, it can result in tooth loss. Modern periodontal treatment is highly effective, and patients often experience significant improvement after the first few procedures.
- Periodontosis: The most dangerous disease, as it often develops without symptoms. However, the consequences are severe, with serious damage to the tissues.
Depending on the characteristics and severity of the disease, timely periodontal treatment is necessary. Modern methods and technologies allow us to quickly localize the disease and stop the inflammation.
Treatment Methods in Periodontology
Modern dentistry has a variety of tools available to halt gum inflammation at any stage. The goal of such treatments is to eliminate bacteria and reduce periodontal pockets to a level where the patient can maintain oral health independently.
After gathering all the necessary information, the periodontist will discuss your gum health and propose the most effective treatment. The key is that the treatment must be comprehensive, addressing all underlying causes and factors that contribute to the disease. Only in this way can we completely heal or stabilize periodontal disease.
At the beginning of treatment, the periodontist needs to remove deposits and eliminate inflammation. This involves ultrasonic and other cleaning methods. The treatment is carried out in several stages, depending on the severity of the disease.
Early Stage: Typically identified during preventive checkups and treated with medication. The patient is prescribed immuno-enhancing medications, as periodontal patients often have weakened immune systems. Anti-inflammatory drugs are also prescribed. Medications may be applied topically or taken orally. The main therapeutic methods for treating periodontitis include closed curettage, smoothing the tooth root surface, Vector therapy, and photodynamic therapy.
Severe Stage: Requires surgical intervention, as the gum has receded, and bone tissue needs to be regenerated. In particularly severe cases, flap surgery is performed. During this procedure, excess tissue caused by loose teeth – pockets and granulations – is removed. Platelet-rich plasma therapy may also be prescribed.
After completing the main course of treatment, the patient will need to attend follow-up checkups every 3 or 6 months, or according to an individual schedule. Regular dental visits are crucial for maintaining stable results.
To prevent serious complications, you can begin preventing inflammation and gum bleeding right now.
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
One of the modern methods of treating periodontal disease is photodynamic therapy, which is frequently used by specialists in our clinic. So, what is this procedure?
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an innovative, non-invasive, and painless treatment method that is successfully applied in dentistry. It provides effective help for all patient categories, including children, pregnant women, and those with allergies.
The PDT procedure is non-invasive, avoids the need for additional antibiotics and antiseptics, and does not cause side effects. It allows patients to either avoid surgical procedures entirely or at least reduce their extent. In most cases, one PDT procedure is enough to achieve the desired positive results. In more complex cases, a follow-up session may be scheduled a week after the first treatment.
The essence of the method lies in the ability of oxygen to destroy microorganisms that cause the formation of periodontal pockets. A special gel is introduced into the periodontal pockets, which “marks” pathogenic bacteria. After 5-10 minutes, the pockets are treated with laser light at a specific wavelength for 1-2 minutes per pocket. As a result of the laser exposure, a photochemical reaction occurs, releasing active oxygen that destroys pathogenic bacteria.
After the procedure, a thin film forms on the gum, serving as a biological dressing that protects the tissues from bacterial infiltration.
After the first procedure, the patient’s condition improves significantly: pain disappears, gum bleeding decreases, and shallow periodontal pockets close. To achieve a stable positive effect, specialists typically recommend a course of four procedures, with a 7-day interval between each.
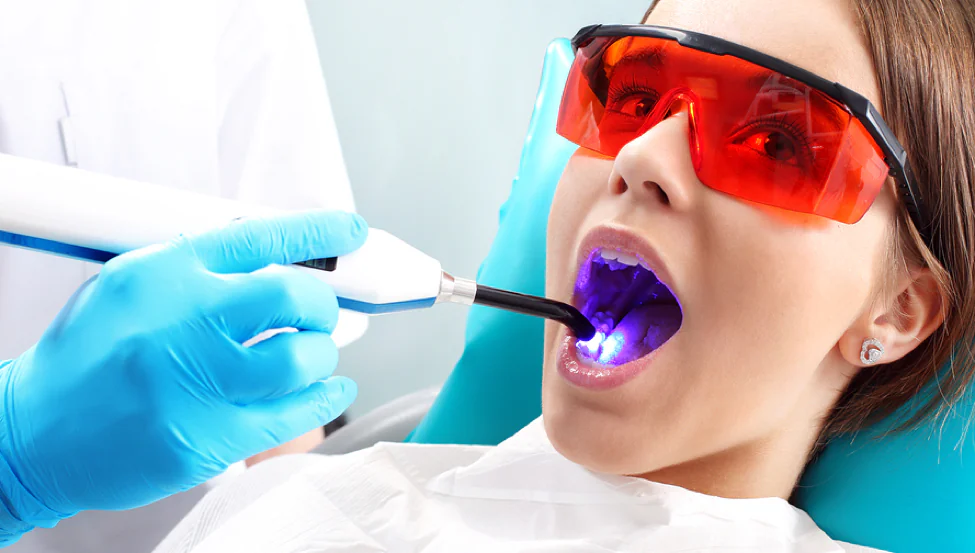
Thus, PDT is a unique tool that allows for simple, fast, and effective elimination of pathogenic bacteria in the periodontium, significantly improving the standard treatment typically offered to patients.
At “Sigma Dent” clinic, qualified specialists with extensive practical experience in treating periodontal diseases are available. Our periodontists will accurately diagnose and prescribe effective gum treatment.
Don’t delay your problems—contact “Sigma Dent” today!

